In Dataverse, Environment Variables store parameter keys and values, which serve as inputs to various other application objects. Since environment variables are considered solution components, you can transport the references (keys) and update the values when migrating solutions to different environments.
In this article, I will provide a C# code snippet that demonstrates how to read the value of an ‘Environment Variable’ using a Query Expression.
Before that lets understand basics.
How Environment Variable value’s gets stored:
Before proceeding, it is essential to understand how the values of ‘Environment Variables’ are stored and managed within the Dataverse environment.
- I’ve created an ‘Environment Variable’ with name ‘autocoe_ValidRolestoFetchAduit’.
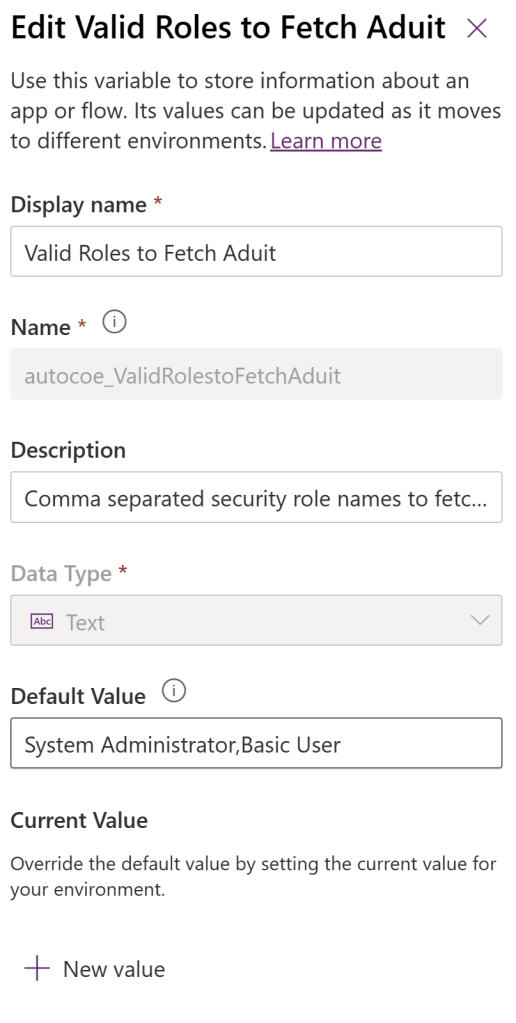
- If you notice above screenshot, there are 2 values, ‘Default Value’ and ‘Current Value’.
- Current Value:
- Also known as the Value. This property is optional and is a part of the Environment Variable Value table.
- When a value is present it will be used, even if a default value is also present.
- Remove the value from your solution if you don’t want to use it in the next environment.
- Default Value.
- This column is part of the Environment Variable Definition table and is not required.
- The Default Value is used if there’s no current value.
- Current Value:
- From above description, the key takeaway is as follows:
- If you set the ‘Current Value’, you need to query the Environment Variable Value table.
- If you don’t set the ‘Current Value’ but you set the ‘Default Value’, you need to query the Environment Variable Definition table.
- If both ‘Current Value’ and ‘Default Value’ are set, we need to use the ‘Current Value’ by querying Environment Variable Value table.
- Coming to my scenario, since I have set the Default Value, I can observe that the record appears in the Environment Variable Definition table.

- Since I did not set the ‘Current Value’, there is no entry in Environment Variable Value table.
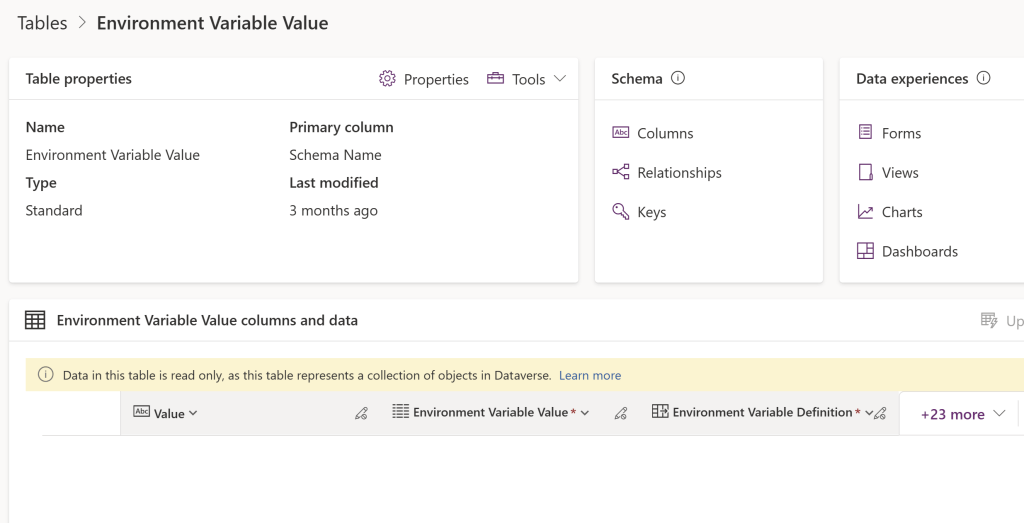
- To understand the Environment Variable Value table significance, lets go ahead and set the ‘Current Value’ as follows.
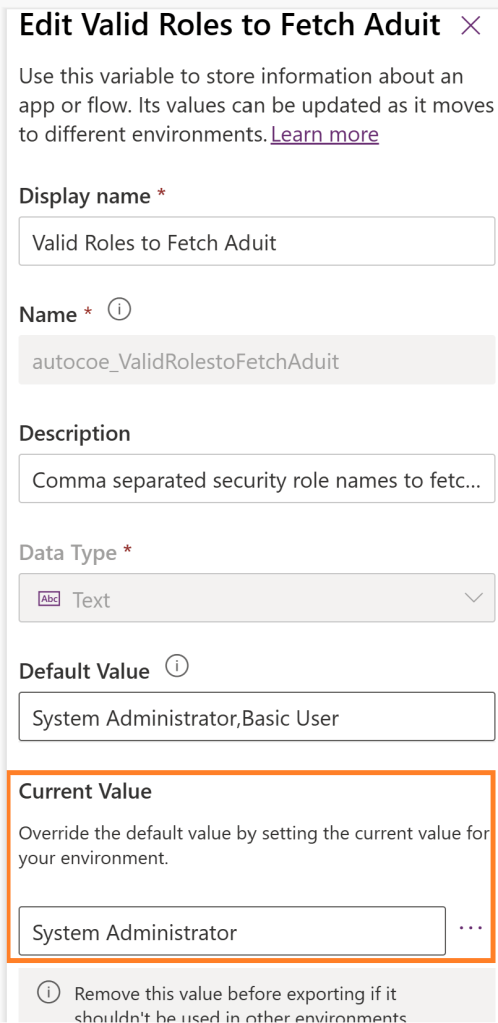
- If you go and check the Environment Variable Value table, you should notice a record.

Now that you have a grasp of the basics, let’s proceed to construct the C# logic. We will start by querying the Environment Variable Value table for Value and If the result is null, we will then query the Environment Variable Definition for Default Value.
Code Snippet:
/// <summary>
/// Gets the value of an environment variable based on the provided schema name.
/// If no matching record with a value is found, it checks for a default value.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="environmentVariableSchemaName">The schema name of the environment variable.</param>
/// <param name="orgService">The IOrganizationService instance used to connect to Dataverse.</param>
/// <returns>
/// The value of the environment variable if found;
/// if no matching record with a value is found, it returns the default value;
/// otherwise, returns null.
/// </returns>
public static string GetEnvironmentVariableValue(string environmentVariableSchemaName, IOrganizationService orgService)
{
string envVariableValue = null;
var query = new QueryExpression("environmentvariabledefinition")
{
ColumnSet = new ColumnSet("defaultvalue", "schemaname", "environmentvariabledefinitionid")
};
query.Criteria.AddCondition("schemaname", ConditionOperator.Equal, environmentVariableSchemaName);
var linkEnvironmentValue = new LinkEntity("environmentvariabledefinition", "environmentvariablevalue", "environmentvariabledefinitionid", "environmentvariabledefinitionid", JoinOperator.Inner)
{
EntityAlias = "EV"
};
linkEnvironmentValue.Columns.AddColumns("value");
linkEnvironmentValue.LinkCriteria.AddCondition("value", ConditionOperator.NotNull);
query.LinkEntities.Add(linkEnvironmentValue);
var result = orgService.RetrieveMultiple(query);
if (result.Entities.Count > 0)
{
Entity entity = result.Entities[0];
if (entity.Attributes.Contains("EV.value"))
{
envVariableValue = entity.GetAttributeValue<AliasedValue>("EV.value").Value.ToString();
}
}
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(envVariableValue))
{
// Check for 'Default Value' in 'environmentvariabledefinition'
envVariableValue = GetDefaultEnvironmentVariableValue(environmentVariableSchemaName, orgService);
}
// Return envVariableValue. It will be null if no matching record with a value or default value is found.
return envVariableValue;
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets the default value of an environment variable based on the provided schema name.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="schemaName">The schema name of the environment variable.</param>
/// <param name="orgService">The IOrganizationService instance used to connect to Dataverse.</param>
/// <returns>The default value of the environment variable if found; otherwise, returns null.</returns>
private static string GetDefaultEnvironmentVariableValue(string schemaName, IOrganizationService orgService)
{
var query = new QueryExpression("environmentvariabledefinition")
{
ColumnSet = new ColumnSet("defaultvalue", "schemaname", "environmentvariabledefinitionid")
};
query.Criteria.AddCondition("schemaname", ConditionOperator.Equal, schemaName);
var result = orgService.RetrieveMultiple(query);
if (result.Entities.Count > 0)
{
Entity entity = result.Entities[0];
if (entity.Attributes.Contains("defaultvalue"))
{
return entity.GetAttributeValue<string>("defaultvalue");
}
}
// Return null if no matching record is found or if 'value' attribute is null.
return null;
}How do I use the code snippet?
- To fetch the Environment Variable value for ‘autocoe_ValidRolestoFetchAduit’, call the ‘GetEnvironmentVariableValue‘ function as below. The result will be captured in ‘environmentVariableValue’ variable.
var environmentVariableValue = GetEnvironmentVariableValue("autocoe_ValidRolestoFetchAduit", orgService);🙂
![[Step by Step] Beginner : Create a PCF control and add it to a custom page](https://rajeevpentyala.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/image-49.png)
![[Step by Step] Configure and run 'Pipelines in Power Platform'](https://rajeevpentyala.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/image.png)

Leave a comment